Ion exchange chromatography is a widely used separation technique in biotechnology, used for the purification of proteins, enzymes, antibodies, and other biomolecules. Ion exchange chromatography relies on the interaction of charged groups on the molecule of interest with charges on the stationary phase, the ion exchange resin.
The choice of resin is critical to the success of the separation process. Resins are typically made of a polymeric material that contains a functional group with an ionizable charge, such as sulfonic acid or quaternary ammonium salt. The choice of resin depends on the pH of the buffer, the strength and charge of the ion to be separated, and the size and shape of the molecule of interest.
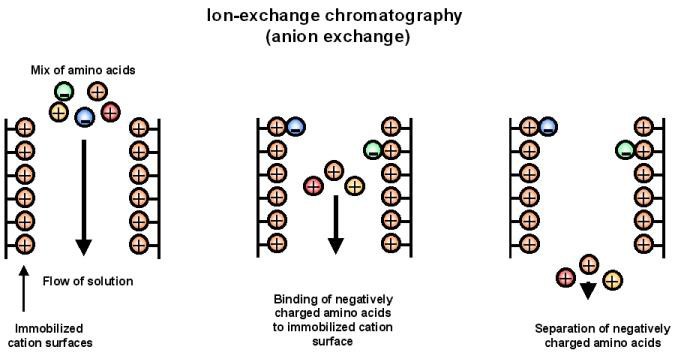
Different types of resin are available for ion exchange chromatography, such as cation exchange resins and anion exchange resins. Cation exchange resins have negatively charged functional groups, such as sulfonic acid, that attract and bind positively charged molecules, such as amino acids and proteins. Anion exchange resins have positively charged functional groups, such as quaternary ammonium salts, that attract and bind negatively charged molecules, such as DNA, RNA, and viruses.
Resin selection is also influenced by the mode of separation, whether it is a batch or a column-based process. In batch mode, the resin is mixed with the sample in a container, and the mixture is stirred, allowing the molecules to exchange ions with the resin. In column-based mode, the resin is packed into a column, and the sample is applied to the top of the column. As the sample flows through the column, the molecules interact with the resin, and the target molecule is eluted based on its charge and size.
In addition to selecting the right resin, the type and concentration of the elution buffer also affect the performance of ion exchange chromatography. The elution buffer is used to release the target molecule from the resin and into solution. The choice of buffer depends on the pH, salt concentration, and polarity of the molecules being separated.
Resin in ion exchange chromatography is an essential component that plays a crucial role in the successful purification of proteins and other biomolecules. The choice of resin is dependent on the specific needs of the separation process, including the type and charge of the molecule to be purified. Therefore, careful consideration of the resin and elution buffer is vital for efficient and high-quality outcomes.


