A water softener is a device that is used to remove minerals that make water hard and cause scaling in pipes, on appliances, and on dishes. But how does it work? In this article, we'll explore the process of water softening and explain how it works.
Water softening is the process of removing the minerals that cause hardness in water, such as calcium and magnesium. These minerals are removed through a process called ion exchange.
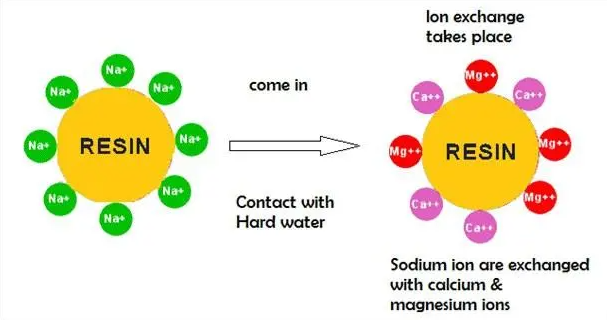
The water softener contains a resin tank that is filled with small beads made of polystyrene. These beads are referred to as ion exchange resin beads. The ion exchange resin beads are charged with sodium or potassium ions.
As the water flows into the resin tank, the calcium and magnesium ions in the water are attracted to the negatively charged resin beads. These ions exchange places with the sodium or potassium ions on the beads, effectively removing the hardness-causing minerals from the water.
Once the resin beads have become saturated with calcium and magnesium ions, they need to be regenerated. Regeneration is the process of flushing out the saturated beads and replacing them with fresh, charged beads. This is done by adding a concentrated solution of saltwater to the resin tank. The saltwater solution is made up of sodium or potassium chloride.
The saltwater flows through the resin tank, replacing the calcium and magnesium ions on the resin beads with sodium or potassium ions. This process regenerates the resin tank and allows it to continue removing hardness-causing minerals from the water.
After the regeneration cycle is complete, the saltwater solution is flushed out of the resin tank, leaving the resin beads charged with sodium or potassium ions once again. This process is automated in most water softeners, so you do not need to do anything.
Water softeners are an effective way to remove hard water from your home's water supply. They ensure that your appliances and plumbing remain scale-free, which can prolong their lifespan. In addition, soft water can be gentler on your hair, skin, and clothing.
In conclusion, water softeners work by removing hardness-causing minerals from water through the process of ion exchange. The resin beads in the water softener tank are charged with sodium or potassium ions, and as water flows through, hardness-causing minerals are exchanged for the sodium or potassium ions. When the resin beads become saturated, they are regenerated with a concentrated saltwater solution. This ensures that your home's water supply remains soft and free of scale.


