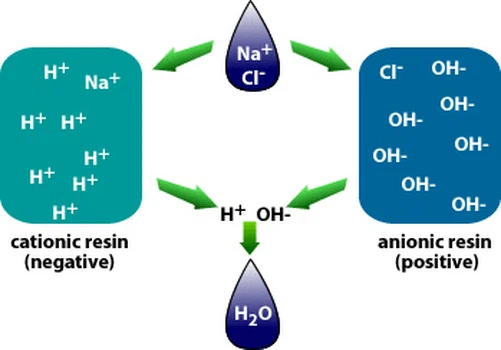
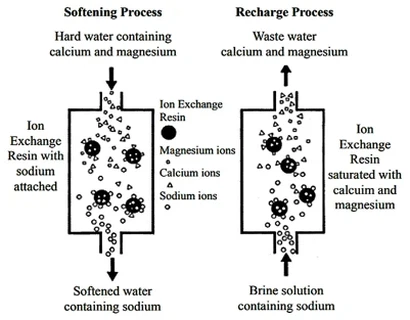
Ion exchange desalt of water is to exchange various cations in water into H+ with H type cation exchange resin, exchange various anions in water into OH- with OH type anion exchange resin, and the H+ and OH- ions entering the water form water molecules H2O, or let the water pass through the Yangyin mixed ion exchange resin layer. The positive and anion in water are replaced by H+ and OH- ions almost simultaneously. In this way, when the water is treated by ion exchange, various inorganic salts in the water can be removed. The H ion exchange reaction and OH ion exchange reaction occurring in the process and the reaction occurring in the resin regeneration process are as follows:
(1) Hydrogen ion exchange reaction formula:
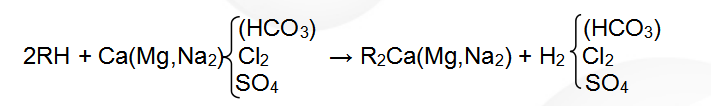
The regenerative reaction formula is:
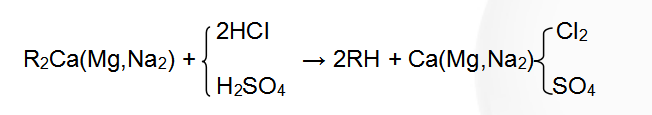
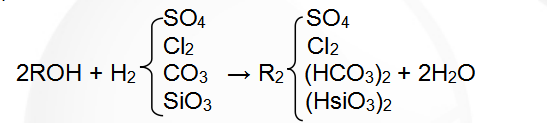
(2) The hydroxide ion exchange reaction equation is:
Regenerative reaction formula:
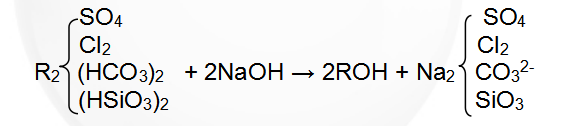
The water entering the ion exchanger usually contains a large amount of bicarbonate. It is a major component of the alkalinity of natural water. When the water is exchanged by H ions, the bicarbonate is converted into carbonic acid, and the carbonic acid originally contained in the water can be removed with a carburizer. This reduces the burden on the anion exchanger and reduces consumption.
The effluent of primary demineralization system: hardness ≈0umol/L, silica ≤100ug/L, conductivity ≤5uS/cm.
Secondary desalting system effluent: silica ≤20ug/L, conductivity ≤0.2uS/cm.